Tag: approximation
-
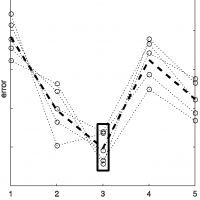 Data-driven approximation algorithms for rapid performance evaluation and optimization of civil structuresStavros Tseranidis, Nathan Brown, and Caitlin Mueller, Automation in Construction: Special Issue "BIG DATA IN CIVIL ENGINEERING", 2016
Data-driven approximation algorithms for rapid performance evaluation and optimization of civil structuresStavros Tseranidis, Nathan Brown, and Caitlin Mueller, Automation in Construction: Special Issue "BIG DATA IN CIVIL ENGINEERING", 2016This paper explores the use of data-driven approximation algorithms, often called surrogate modeling, in the early-stage design of structures. The use of surrogate models to rapidly evaluate design performance can lead to a more in-depth exploration of a design space and reduce computational time of optimization algorithms. While this approach has been widely developed and used in related disciplines such as aerospace engineering, there are few examples of its application in civil engineering. This paper focuses on the general use of surrogate modeling in the design of civil structures and examines six model types that span a wide range of characteristics. Original contributions include novel metrics and visualization techniques for understanding model error and a new robustness framework that accounts for variability in model comparison. These concepts are applied to a multi-objective case study of an airport terminal design that considers both structural material volume and operational energy consumption.
-
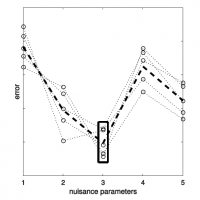 Approximation algorithms for rapid evaluation and optimization of architectural and civil structuresStavros Tseranidis, MIT SM thesis, 2015
Approximation algorithms for rapid evaluation and optimization of architectural and civil structuresStavros Tseranidis, MIT SM thesis, 2015This thesis explores the use of approximation algorithms, sometimes called surrogate modelling, in the early-stage design of structures. The use of approximation models to evaluate design performance scores rapidly could lead to a more in-depth exploration of a design space and its trade-offs and also aid in reducing the computation time of optimization algorithms. Six machine-learning-based approximation models have been examined, chosen so that they span a wide range of different characteristics. A complete framework from the parametrization of a design space and sampling, to the construction of the approximation models and their assessment and comparison has been developed. New methodologies and metrics to evaluate model performance and understand their prediction error are introduced. The concepts examined are extensively applied to case studies of multi-objective design problems of architectural and civil structures. The contribution of this research lies in the cohesive and broad framework for approximation via surrogate modelling with new novel metrics and approaches that can assist designers in the conception of more efficient, functional as well as diverse structures.


